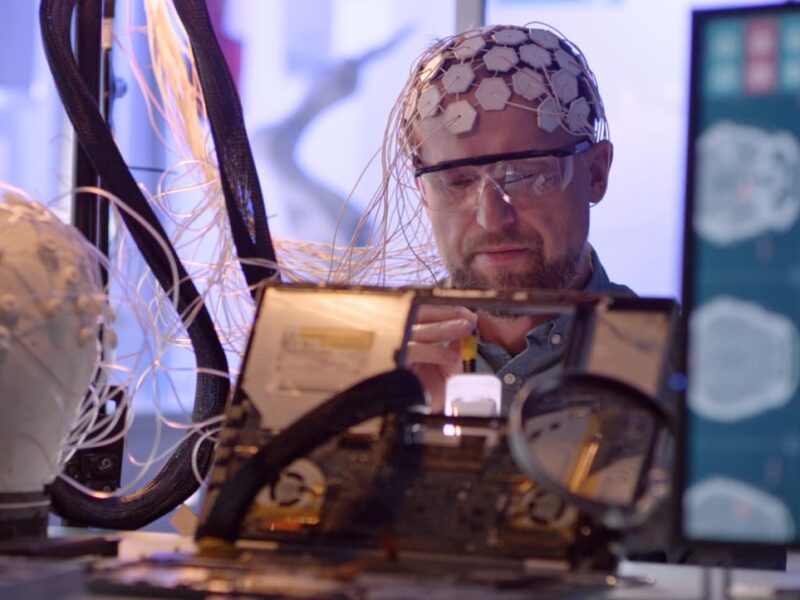
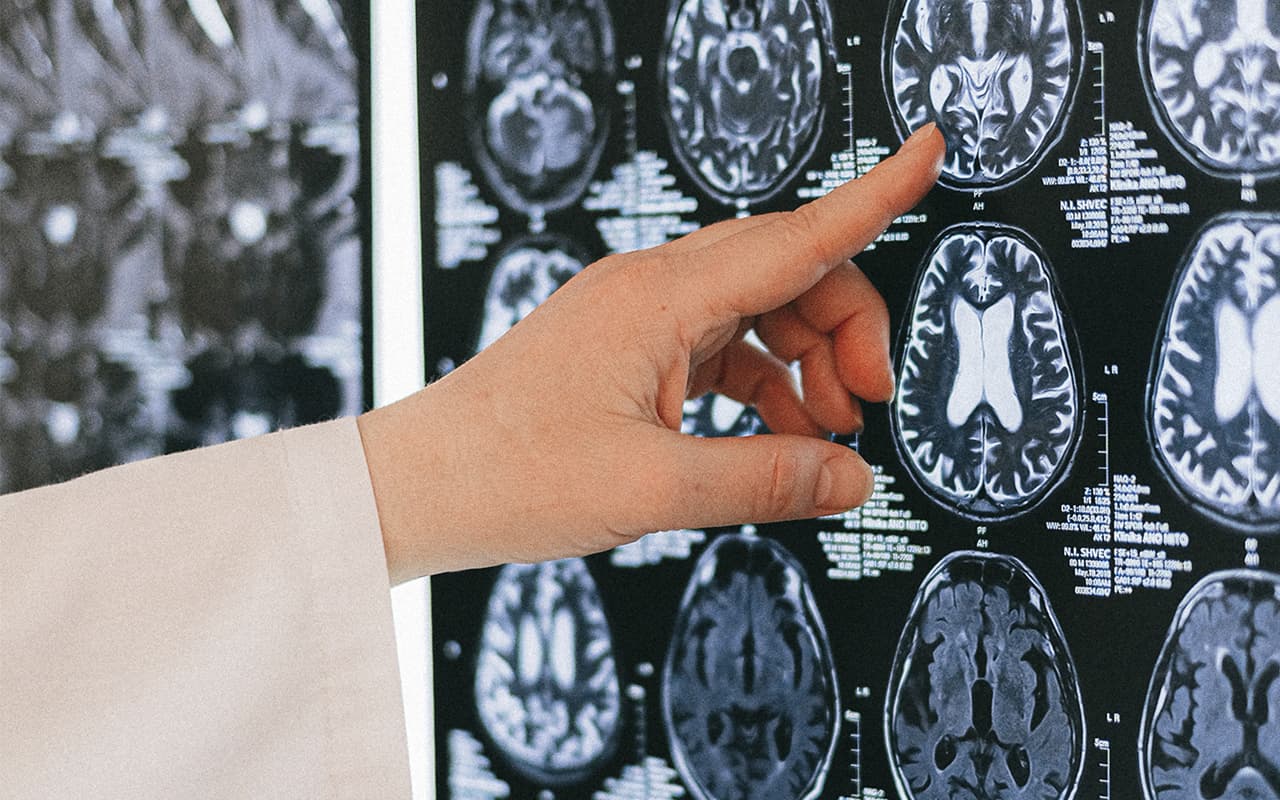
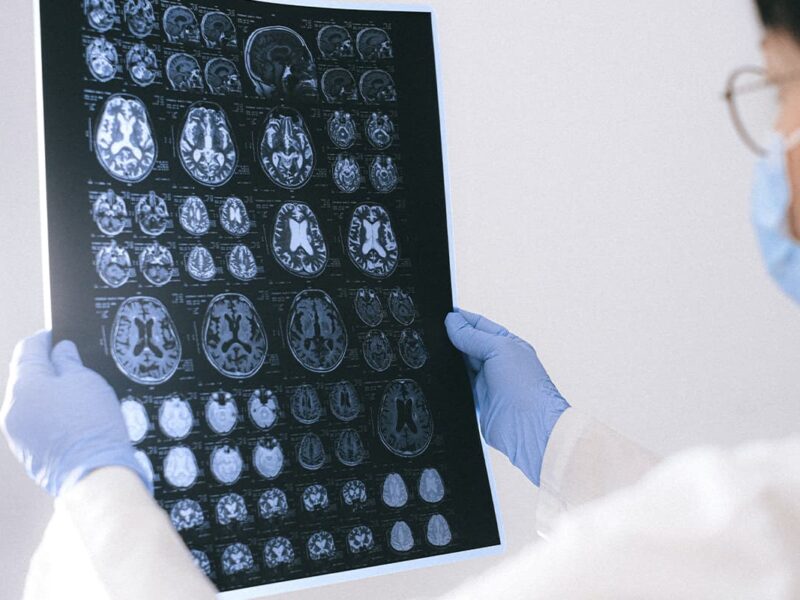
Neurobiology is the science that seeks to understand how the nervous system is organized and functions. The vertebrate nervous system includes both the central and peripheral nervous system. The central nervous system consists of the brain and spinal cord. The peripheral nervous system consists of nerves outside the central nervous system.
Basic neurobiology at the tissue level involves the study of neurons, glial cells, and the extracellular matrix. Neurons are the cells of the nervous system that are involved in information processing. Glial cells provide nourishment, protection, and structural support to neurons. The extracellular matrix in the brain provides life support at the molecular level for both neurons and glial cells. A specialized type of glial cells – astrocytes – are of particular interest to researchers, as they are the most numerous population and perform many important functions: maintenance of extracellular homeostasis, formation of the blood-brain barrier, glycogen storage, participate in neurogenesis and synaptogenesis, etc. These cells and extracellular matrix are the constituents of the nervous system.
Research in neurobiology studies inter-neuronal interactions, synaptic signal transduction through neurotransmitters, functional organization of the nervous system, and information processing mechanisms. Scientific studies of phylogenesis and early stages of ontogenesis of the nervous system investigate the processes of nerve cell formation, acquisition of functions in norm and pathology
The organization of afferent and efferent systems of higher vertebrates and humans, biomechanisms of higher integrative and behavioral functions are studied.