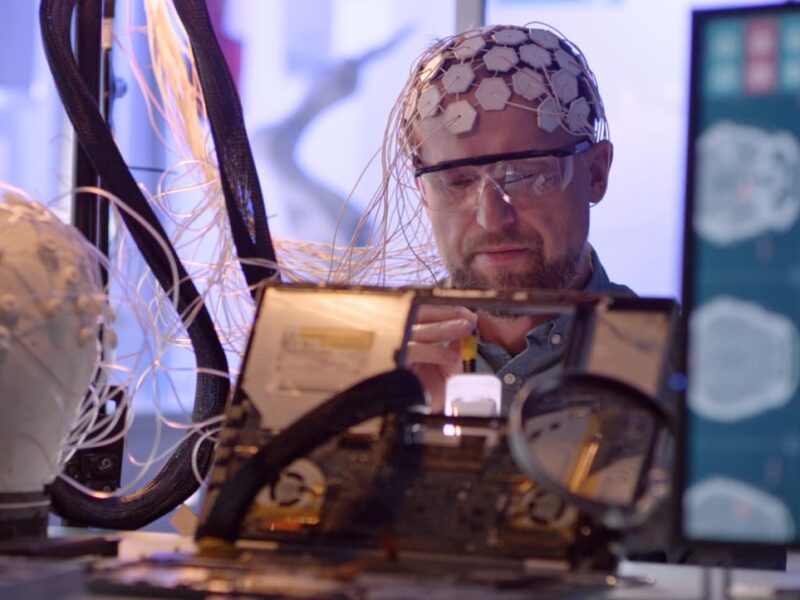
Behavioral neurobiology: an interdisciplinary branch of behavioral neurobiology. Also called biological psychology, biopsychology, psychobiology, or neuroethology. Specialists in this field investigate how biological mechanisms in the central nervous system control behavior, learning, and memory.
Developmental neurobiology: a specialized section of neurobiology. Scientists in this field study the processes that contribute to brain development and function. It all starts with a few specialized embryonic cells that transform into the nervous system. Specialists study how these cells change before forming a functional nervous system. Such research may improve understanding of the mechanisms of development of some neurological disorders.
Molecular biology. Researchers in this field study neuroanatomy at the molecular level and how molecular interactions contribute to the nervous system. They also study the influence of genetics on neuronal development and the molecular basis of neuroplasticity and neurodegenerative diseases. This is a relatively new and dynamic field.
Neurobiology of addiction: a specialized branch of neurobiology that studies the mechanisms of neuronal connectivity disorders in the development of addiction. Studies using neuroimaging are important in understanding the key changes in the human brain that contribute to the development of addiction.
Neurobiology of aging: a specialized section of neurobiology. Researchers in this field study the physiological aging processes of the brain, focusing on the mechanisms of nervous system changes with age or age-related diseases such as epilepsy, Alzheimer’s disease, and age-related memory impairment. These studies pay attention to changes in synaptic connections as neurons die off, the influence of the endocrine system and electrolytes, particularly calcium, both in normal brain aging and in neurodegenerative diseases.
Neurobiology of anxiety disorders. Researchers in this field study changes in neuronal, neuroendocrine, and neurotransmitter activity in anxiety and depression. Scientists are primarily interested in those areas of the brain in which the greatest changes occur. This research contributes to the development of effective treatments and prevention of anxiety disorders.
Autism neurobiology: a specialized branch of neurobiology that studies the developmental factors in the nervous system that contribute to autism spectrum disorders (ASD). Research focuses on genetic mechanisms, brain developmental processes, and the relationship between neuroanatomical brain regions associated with the onset of autism.
Neurobiology of Mental Disorders: Researchers in this field seek to understand the role of neurotransmitters in the formation of mental disorders using molecular genetics techniques. One of the challenges that researchers face in studying this field is the lack of patients for the control group who are not currently taking psychotropic medications when the disorder relapses.
Neurobiology of bipolar disorder: a specialized section of neurobiology and psychiatric disorder research. The complex nature of bipolar disorder’s oscillation between mania and depression makes it difficult for researchers to identify its causes. Researchers study the brain connections and neurotransmitter systems that contribute to the development of this disorder.
Neurobiology of mental trauma. Researchers in this field study the interrelationships of different brain regions with endocrine and neurotransmitter responses to traumatic exposure. These effects are studied in the short and long term at the molecular, cellular, and behavioral levels. Research in this area overlaps with the developmental neurobiology of childhood trauma or negative childhood experiences (NDEs).
Sleep neurobiology. Researchers in this field study the nervous system functions involved in the processes of sleep and wakefulness and the genetic and behavioral factors that regulate sleep. Discoveries in this field contribute to the understanding and treatment of circadian rhythm and sleep disorders.